
This technique develops tools for calming the body and mind when confronted with germs. In so doing, you form the capacity to be around germs without feeling compelled to disinfect yourself. With frequent and gradually more intense exposures, you concentrate on calming techniques and are discouraged from washing your hands. In this case, germ exposure might be in the form of touching dirt or you might begin with something less challenging such as touching plants planted by someone wearing gloves that touched dirt. This form of treatment involves exposing oneself to germs. Each treatment will occur under the supervision and assistance of a therapist. This form of therapy uses three major treatments: cognitive restructuring, exposure therapy, and relaxation training, at times in combination and at times individually based on the desires and needs of the client. Talk to a mental health expert or your physician about the medications or therapy approaches that could help you with anxiety management and decrease obsessive behaviors that hinder your life.
PATHOLOGICAL FEAR OF GUMS PROFESSIONAL
It’s hard to conquer a phobia without professional help. Also, don’t feel embarrassed to inform family and friends regarding your phobia and how they can offer support during treatment. Online and in-person support groups can be encouraging in the lives of those who desire to manage their anxiety concerning germs.
Millions suffer from a particular phobia, so take some time to establish the support that’s available in your community. Moreover, education can give you a feeling of general hygiene prerequisites so that you can assess your behaviors with what a doctor might recommend. Watching videos or reading about how bacteria forms a natural part of your environment and body can help you manage worry and fear.

One challenge of overcoming this phobia is learning to change the irrational thoughts you have regarding contamination and germs. Some home remedies and lifestyle changes might help alleviate your fear of germs. Gradually, sufferers might impose numerous limitations upon themselves, for instance, declining to touch doorknobs or shake hands.
PATHOLOGICAL FEAR OF GUMS SKIN
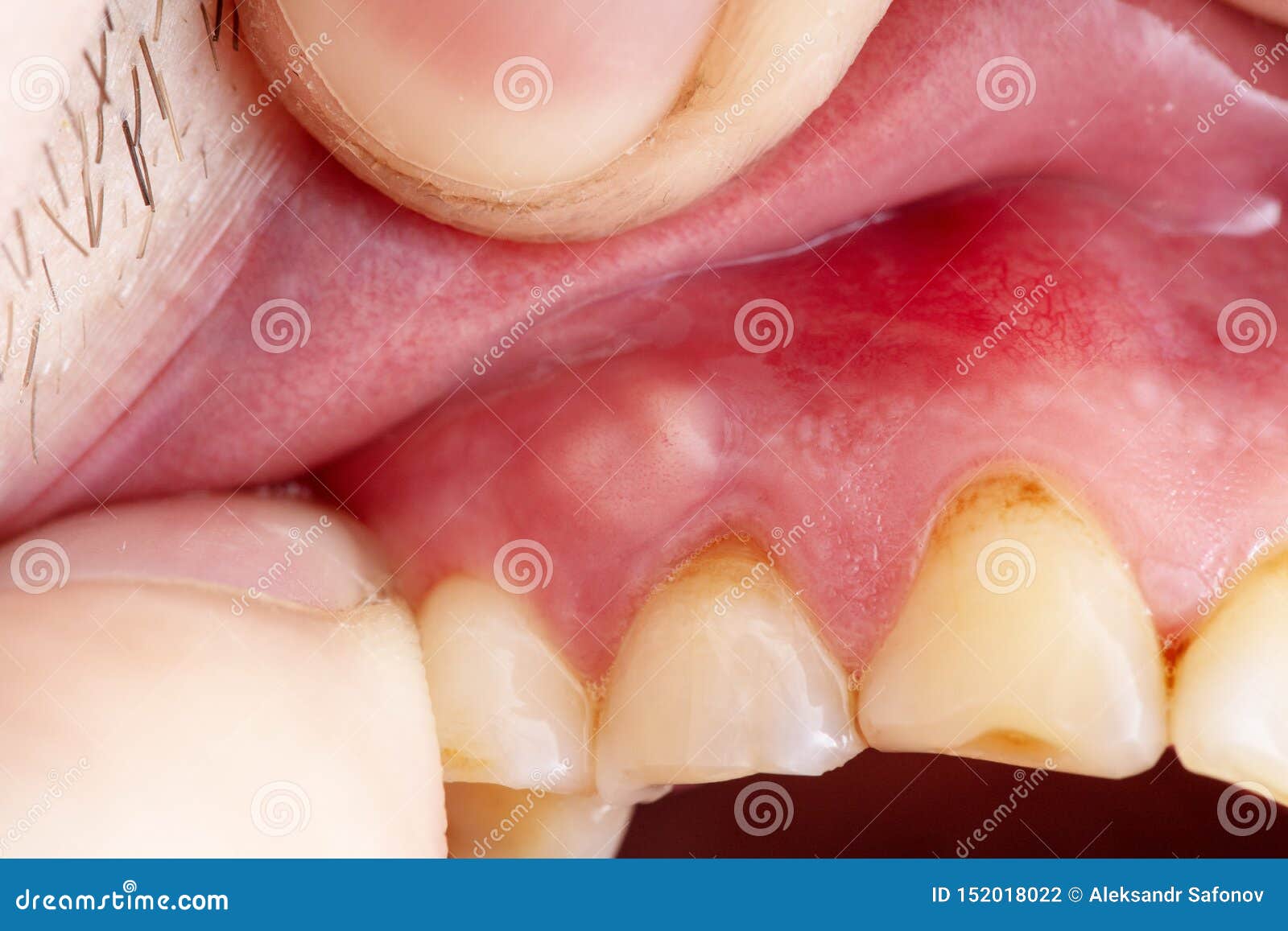
Persistent washing could lead to red, cracked, dry, or irritated skin as well as discomfort and skin lesions, which are susceptible to infection and bleeding. Time-consuming and excessive cleaning, ritualized bathing and showering to eliminate perceived germs and dirt, extreme grooming, toothbrushing, and continuously focusing on evaluating infection threat take their toll. Decontamination compulsions tend to consume their lives. Germaphobes also typically have cleaning and washing compulsions and avoid possible contaminants.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
